

Two carriers have a 25% chance of having an unaffected child with two unaffected genes. Their health is rarely affected because they have only one changed gene.

To have an autosomal recessive disorder, you inherit two changed genes, sometimes called mutations. If you have symptoms that could be porphyria, get medical attention. This can make it difficult to know if you're having an attack of porphyria. Many symptoms of porphyria are like those of other, more common conditions.
#Diogenes syndrome symptoms skin
Repeated exposures can cause thick, leathery skin and scarring. Sun or artificial light exposure quickly results in painful skin burning, irritation and swelling. It's the most common childhood porphyria. Too much hair growth in affected areas.Įrythropoietic protoporphyria (uh-rith-roe-poi-ET-ik pro-toe-por-FEAR-e-uh), also called EPP, is a rare type of cutaneous porphyria.Fragile thin skin with changes in skin color.Blisters on exposed skin, usually the hands, arms and face.Sudden painful skin redness and swelling.Sensitivity to the sun and sometimes artificial light, causing burning pain in the skin.Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is the most common type of all the porphyrias. These forms usually don't affect the nervous system. Rapid or irregular heartbeats you can feel, called palpitations.Ĭutaneous porphyrias include forms of the disease that cause skin symptoms as a result of sensitivity to sunlight.Mental changes, such as anxiety, hallucinations or mental confusion.
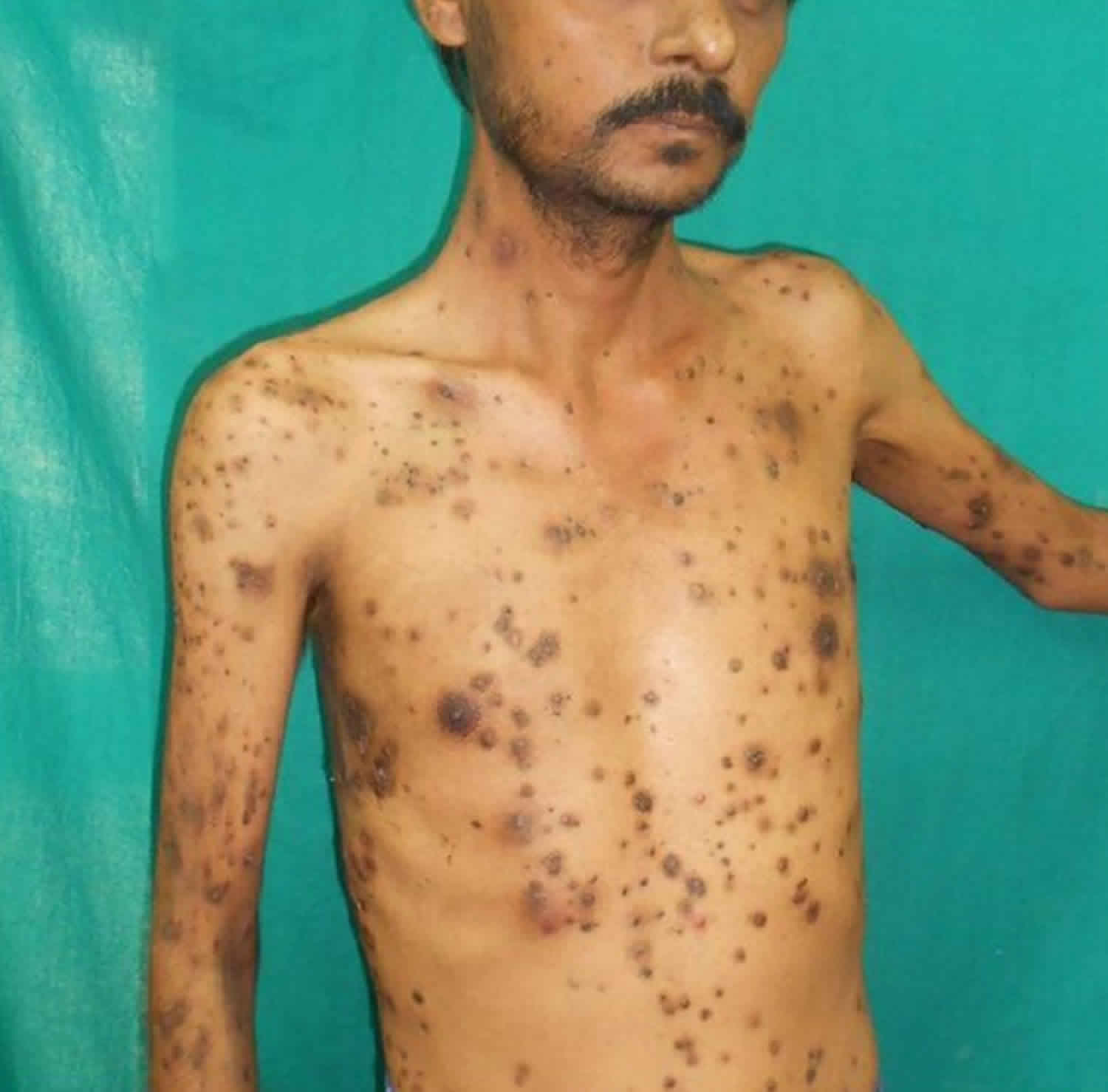
Muscle pain, tingling, numbness, weakness or paralysis.Digestive problems, such as constipation, nausea and vomiting.Severe pain in the belly, chest, legs or back.Symptoms of acute porphyrias may include: When the symptoms occur they are sometimes called attacks. Intermittent means that the symptoms may go away but return later. The most common form of acute porphyria is called acute intermittent porphyria (AIP). Symptoms appear quickly and can be severe. Acute porphyriasĪcute porphyrias include forms of the disease that usually cause nervous system symptoms. Some people with a gene change that causes porphyria never have any symptoms. Symptoms also can vary among people with the condition. Symptoms can vary widely by type of porphyria and in how severe the symptoms are.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
